Intranet Video Conferencing Software
 Any video conferencing system consists of the following parts:
Any video conferencing system consists of the following parts:
- Video conferencing endpoints, which can be absolutely any devices that support video and audio transfer: hardware, software or mobile systems, sophisticated telepresence systems or even modernly equipped refrigerators;
- Video conferencing servers, required for group video conferences;
- Infrastructure – communication channels, communication units and secondary equipment for broadcasting and recording video etc.;
- Peripheral equipment – speakerphones, mixers, microphones, PTZ-cameras etc.
What Modes of Video Conferences Are There?
- Video call, which is a modes of conference that involves connection between two participants.
 Video conferencing server in this case is optional.
Video conferencing server in this case is optional. - Group video conference is a multipoint video conferencing session involving three or more subscribers. To create a group video conference, you must have a server that will interchange calls as well as transmit video and audio data. Such group video conferences can be divided into symmetric and asymmetric (video lectures and virtual meetings).
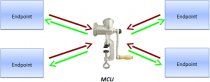 Video Conferencing Server Architecture
Video Conferencing Server Architecture
All solutions are divided into two groups:
- Hardware solutions, that usually reencode video streams from each participant, which requires a lot of CPU resources.
- Software solutions. They do not reencode video streams and the CPU resources are occupied only for data transmission.
Hardware solutions are often based on modules with DSP-processors to support massive computing. The solutions’ capacity may be increased by adding new modules. Such solutions are more expensive.
Software video conferencing solutions do not require video transcoding, so they can be built on the basis of general-purpose processors. They are much simpler and therefore more accessible.
See also:- Find out Benefits of spirulina
You might also like

|
Hawking Technology DC320 3-in-1 PocketCam Digital Webcam CE (Hawking Technology)
|